Network Generations From 1G to 5G: A Brief History and Their Evolution

In this article, we will take a journey through the history of mobile network generations, from the first generation (1G) to the latest fifth generation (5G). We will explore how these networks have evolved over time, their features, and their impact on our daily lives.
Introduction
Mobile Networks Generations have come a long way since their inception, evolving from the basic voice-only networks of the first generation to the super-fast and ultra-reliable networks of the fifth generation. Today, mobile networks are an integral part of our daily lives, providing us with high-speed internet, video streaming, and more. In this article, we will explore the evolution of mobile networks, their features, and their impact on society.
1G: The First Generation
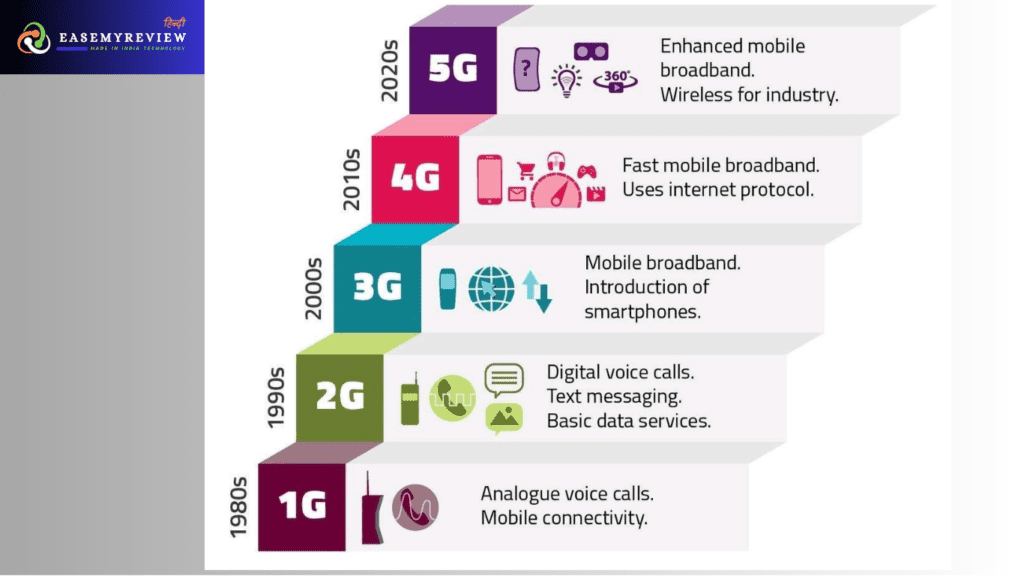
The first network generations of mobile networks, also known as 1G, was introduced in the 1980s. These networks were primarily analog, and they were used for voice calls only. The first 1G network was launched in Japan in 1979, and it was followed by other countries, including the United States and Europe.
2G: The Second Generation
The inception of the 2nd network generations of mobile networks, which is also known as 2G, occurred during the 1990s, marking a major turning point in the evolution of mobile telecommunications. These networks were primarily digital and enabled the transfer of data in addition to voice calls. The first 2G network was launched in Finland in 1991, and it was followed by other countries, including the United States and Europe.
3G: The Third Generation
In the early 2000s, the mobile telecommunications industry saw the emergence of the 3rd generation of mobile networks, commonly referred to as 3G. These networks were faster and more reliable than 2G networks, enabling high-speed internet and video calling. The first 3G network was launched in Japan in 2001, and it was followed by other countries, including the United States and Europe.
4G: The Fourth Generation
The mid-2000s marked the arrival of the fourth generation of mobile networks, known as 4G, which represented a significant step forward in the evolution of mobile telecommunications. These networks were even faster and more reliable than 3G networks, enabling high-definition video streaming and online gaming. The first 4G network was launched in Sweden in 2009, and it was followed by other countries, including the United States and Europe.
5G: The Fifth Generation
The fifth generation of mobile networks, or 5G, was introduced in the early 2010s. These networks are the fastest and most reliable mobile networks ever created, enabling super-fast internet speeds, low latency, and the Internet of Things (IoT). The first 5G network was launched in South Korea in 2019, and it has since been followed by other countries, including the United States and Europe.
Read More – Lava Blaze all about Specs, Sale, Price & More
Key Features of 5G
Several notable attributes characterize 5G networks, including:
High-speed internet
5G networks are capable of providing internet speeds up to 20 times faster than 4G networks, enabling ultra-fast downloads and uploads.
Low latency
One of the defining characteristics of 5G networks is their remarkably low latency, resulting in negligible delays between data transmission and reception. This makes them ideal for real-time applications like online gaming and video calling.
Massive connectivity
5G networks are designed to connect a massive number of devices simultaneously, enabling the Internet of Things (IoT).
Impact of Mobile Networks on Society
Mobile network generations have had a profound impact on society, transforming the way we communicate, work, and play. With the advent of 5G networks, we can expect even more radical changes in the coming years.
Communication
Communication is one of the primary functions of mobile networks, and each generation has brought significant advancements in this area. The first-generation (1G) networks were analog and used for voice calls only, while second-generation (2G) networks introduced digital signaling, enabling text messaging and basic data services.
Third-generation (3G) networks brought faster data transfer speeds, enabling multimedia messaging, mobile internet browsing, and video calling. Fourth-generation (4G) networks brought even faster internet speeds, lower latency, and improved call quality, enabling the widespread adoption of mobile video streaming and social media.
With the advent of 5G networks, we can expect even more significant improvements in communication. 5G networks are capable of ultra-fast internet speeds, low latency, and massive connectivity, making it possible to support a vast number of connected devices and real-time communication. This means that we can expect new communication technologies and services, such as real-time language translation, virtual reality conferencing, and advanced video calling.
In addition to these advancements in communication, 5G networks also bring significant improvements in other areas, such as healthcare, transportation, and smart cities. The low latency and massive connectivity of 5G networks make it possible to support advanced technologies like remote surgery, autonomous vehicles, and real-time monitoring of city infrastructure.
Work
Mobile networks have also transformed the way we work, making remote work and collaboration easier than ever before. With 5G networks, we can expect even more seamless remote work and virtual collaboration, as well as the adoption of new technologies like augmented and virtual reality.
Entertainment
Mobile network generations have also revolutionized the entertainment industry, enabling on-the-go video streaming, online gaming, and social media. With 5G networks, we can expect even more immersive entertainment experiences, such as augmented and virtual reality gaming and real-time streaming of 4K and 8K video.
Conclusion
From the first-generation analog networks to the ultra-fast and reliable 5G networks of today, mobile networks have come a long way in just a few decades. With each new generation, we have seen a dramatic increase in speed, reliability, and connectivity, transforming the way we communicate, work, and play. As we continue to innovate and advance mobile networks, we can expect even more exciting developments in the years to come.
FAQs
- What is a mobile network?
A mobile network is a wireless communication network that enables mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, to connect to the internet and other mobile devices.
- What is the difference between 1G and 5G networks?
1G networks were analog and used for voice calls only, while 5G networks are digital and capable of ultra-fast internet speeds, low latency, and massive connectivity.
- When was the first 1G network launched?
In 1979, Japan inaugurated the initial 1G network, marking a groundbreaking development in the realm of mobile telecommunications.
- What are some key features of 5G networks?
Some key features of 5G networks include high-speed internet, low latency, and massive connectivity.
- How have mobile networks impacted society?
Mobile networks have transformed the way we communicate, work, and play, making communication more accessible, enabling remote work and collaboration, and revolutionizing the entertainment industry.





